Software as a Service (SaaS) is an operating model for software in which the software is installed and operated on a service provider's servers instead of on the user's own computers. Users access the applications via the Internet. SaaS usually runs as a web application in the browser, sometimes via a separate desktop or mobile application that provides access to the actual main application. SaaS is thus a cloud technology.
Software by subscription
Companies outsource IT services with SaaS. As a result, the operating model is usually subscription-based, with the customer paying a fixed amount monthly or annually for use of the application. In this respect, the price includes the software licenses, the infrastructure for deployment and further development. A service contract, known as a service level agreement (SLA), defines the services to which the customer is entitled. This includes, for example, availability of the application, data protection, data backup and recovery, technical support, and compensation in the event of service violations.
Popular examples of software as a service include email services such as Gmail, office software such as Office 365 and Google Docs, CRM systems from Salesforce, and multimedia applications from Adobe.
Graphic source: medium.com
SaaS advantages
Cost-effective resource-saving start-up
When using SaaS, a company does not have to buy software and therefore does not have to maintain its own resources for installation, maintenance and scaling. This eliminates the need for high initial investment and commitment of company resources for the operation of the software. This means that even small companies can always benefit from the current state of development of complex software tools without any problems. Consequently, the deployment time of SaaS applications is also very short.
Scalability for changing requirements
SaaS services can be easily scaled to meet changing business needs. The required service can be obtained at short notice, even if demands increase in the short term.
Mobility for location independence
Access via the Internet allows users to work with the software at any location with an Internet connection. Therefore, users gain mobility this way.
Automatic continuous update
Through SaaS, companies always have the current development status of the application. SaaS applications are usually updated more frequently than traditional software, such as weekly or monthly. This is consequently facilitated by several factors:
- The application is centrally hosted so that an update does not have to be performed by the user. Updates introduced by the provider are automatically available to all users at the same time.
- The SaaS provider does not have to spend resources on updating and maintaining older software versions (as in the case of continuing to maintain older versions of Windows, for example) because there is only ever one version.
- The application provider has extensive access to usage and performance data, which accelerates targeted further development.
Device-independent uniformity of use
The uniform software versions - regardless of the device with which the application is used - facilitate the work of individuals as well as collaboration. The access rights to data and functions required for a user's particular work and role can be managed centrally, enabling security policies to be implemented.
Included data security
The cloud concept relieves companies of business-critical tasks such as data backup and disaster recovery of application data. The data is usually mirrored at several redundant locations of the cloud provider.
Disadvantages SaaS for the user
Long-term costs
A SaaS subscription can be more expensive in the long run than buying the software.
Productivity dependent on internet connection
SaaS applications require Internet access because productivity can depend on the quality of the connection.
Cloud data vulnerability
Since corporate data can be accessed via the Internet when using SaaS, there is a possibility of cyberattacks on sensitive information.
Control dispensing
When using SaaS applications, the work data of the customer company is stored on the servers of the SaaS cloud provider. The implementation of data protection and data security in the cloud is beyond the control of the customer.
Conclusion and outlook SaaS solutions
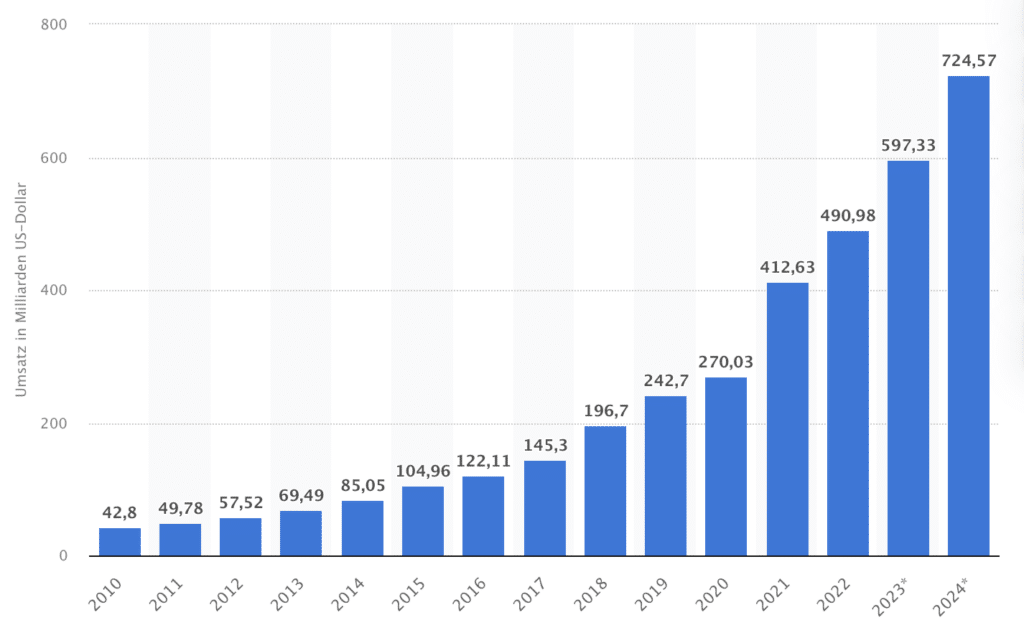
SaaS provides companies with consistently maintained high-quality applications at low entry costs. Consequently, these advantages have led to a continuously growing spread of this software operating model. Market research companies have estimated global revenue from Software as a Service at just under EUR 250 billion in 2023. For the next five years, market analysts expect an annual growth rate of over 7%. (Source: Statista GmbH)






